
ship navigation | ship navigation | true north | truth north | navigating at sea | marine magnetic compass | chapter 2 | part a
Directions on Earth (Courses and Bearings)
Four principle references for direction:
1- True north
2- Compass north and magnetic north
3- Gyro north
4- Ship’s longitudinal axis (in case of relative bearings)
Important definitions:
1- Course
2- Course line
3- Heading
4- Bearing
1- Course:
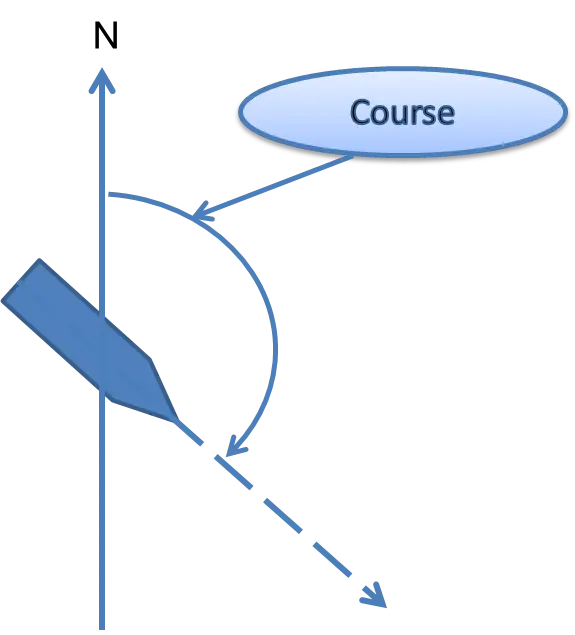
measured from 000° clockwise through 360°
Is often designated as true course, magnetic course, compass course and gyro course
2- Course Line:
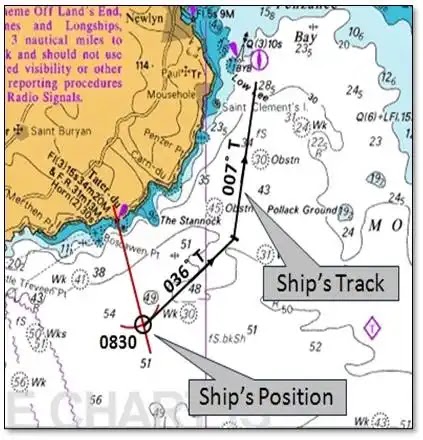
3- Heading:
4- Bearing:
Relative Bearing:

Types of marine compasses

1- Magnetic compass
2- Gyro compass
1- The magnetic compass

Errors of the Magnetic compass
The Magnetic Compass has a total error (Variation + Deviation)
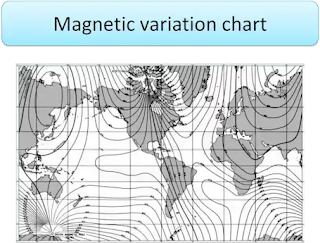
Variation
Terrestrial Magnetism:

It is called easterly (E) if the compass needle, aligned with the magnetic meridian, points eastward or to the right of true north, and westerly (W), if it points to the left

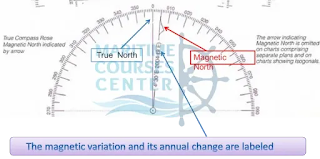
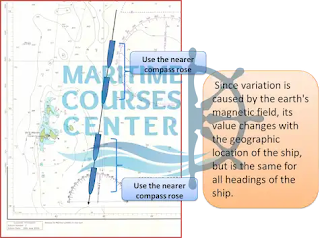
It is obtained from the compass rose on on the chart and must be corrected to the present year.
Compass Rose
Deviation
The divergence caused between the north-south axis of the compass card and the magnetic meridian is called deviation
If deviation is present and the north point of the compass points eastward of magnetic north, the deviation is named easterly and marked E
If it points westward of magnetic north, the deviation is named westerly and marked W.
It is the angle between the magnetic north and the compass north.
It is obtained from the deviation tables.

Deviation tables
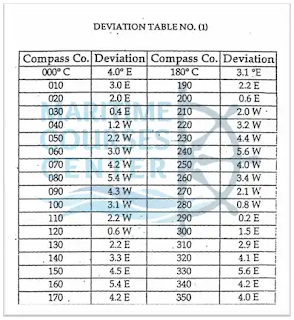
Enter the table with the ship’s compass course and extract the deviation for this compass course



3 Comments