welcome to Marine Courses Center today we will discuss marine engineering & nautical engineering & naval architecture and marine engineering
Marine Engineering Knowledge
Lecture 1
Classification of ships:
1-According to usage:
Cargo ships – passenger ships – service ships – fishing ships – military ships – pleasure boats
2- According to manufacturing materials:
The main material which is used for building is considered as classification type such as wooden ships, steel ships, fibre glass boats, aluminium boats, and rubber boats.
3-according to engine type :
Ships’ main engines could be Diesel engines, Steam turbine, Gas turbine, electric, nuclear, or wind driven ships.
4- According to thrust type:
Sail boats, jet boats, rowing boats, and ships with propellers.
5- According to sailing area:
River ships, coastal ships, overseas ships .
Types of ships:
- General cargo ships: carry dry cargo ( general cargo)
- Container ships: carry containers
- Bulk ships: carry free fall cargo like grain and coal
- Ro-Ro ships ( car carrier ships): carry cars and trucks
- Life stock carriers: carry life animals like sheep, goats, and cows.
- Oil tankers: carry crude oil
- Refrigeration ships : carry refrigerated and frozen cargo.
- LNG ( liquefied natural gas ): carry compressed natural gas in low temperature
- Passenger ships: carry people and their cargo
Engine room layout:
The ship is divided to compartments separated by bulkheads .
Engine room is one of these compartments , mostly located aft of the ship.
Main Engine and propeller shaft:
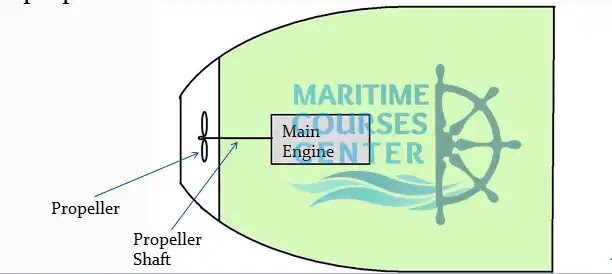
Main engine produce a torque which is transmitted to the propeller through propeller shaft, The thrust from the propeller is transmitted to the ship’s hull through thrust block and causes the ship to be propelled in the direction of the thrust .
Steering Gear:

Steering gear function is to steer the ship to the direction given by the operator.
Electric Generators:
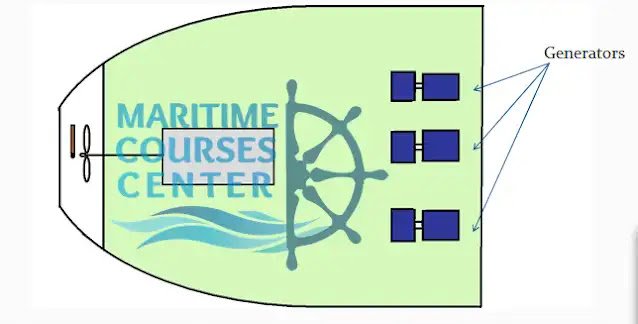
Generators produce required electric power which drives most of ship’s equipment’s .
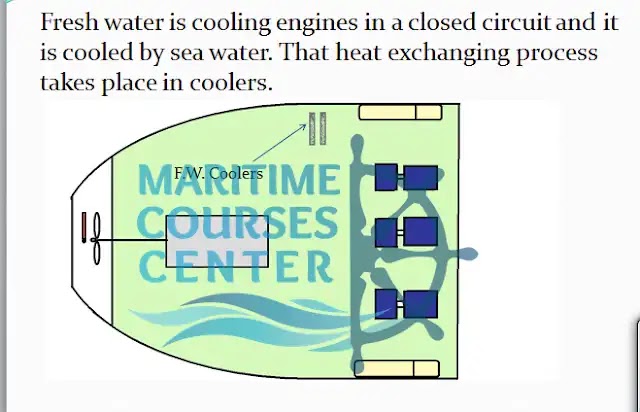
F.W. Coolers:
Fresh water is cooling engines in a closed circuit and it is cooled by sea water. That heat exchanging process takes place in coolers.
Sea water cooling pumps:
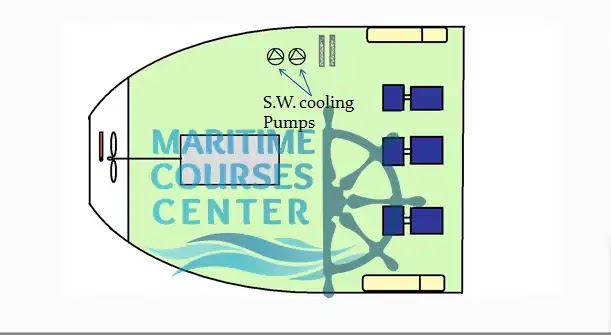
They are used to suck sea water from sea chest passing through the coolers back to sea.
F.W. cooling pumps:
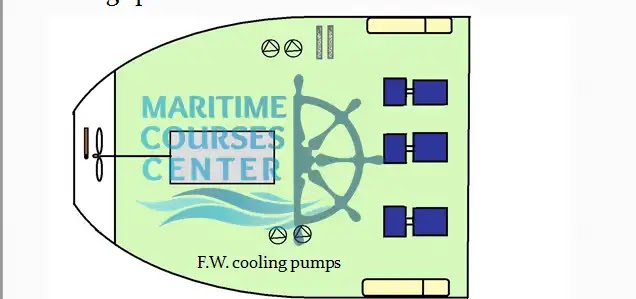
Some types of engines have attached F.W. cooling pumps and some use separated pumps which circulate F.W. From F.W. coolers to engine’s cooling spaces and back to coolers.
Air compressors :
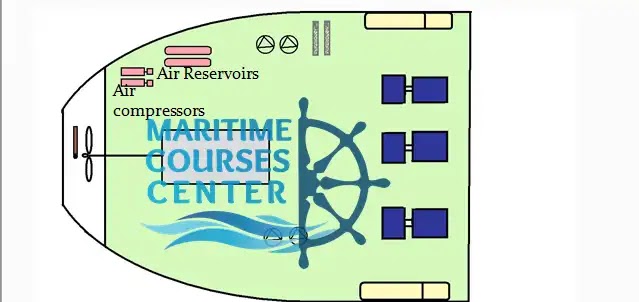
Air compressors suck air from atmosphere and compress it into air reservoirs with about 30 bar . This compressed air is used for starting engines and control air system and for other purposes like operating of air driven tools
L.O. pumps:
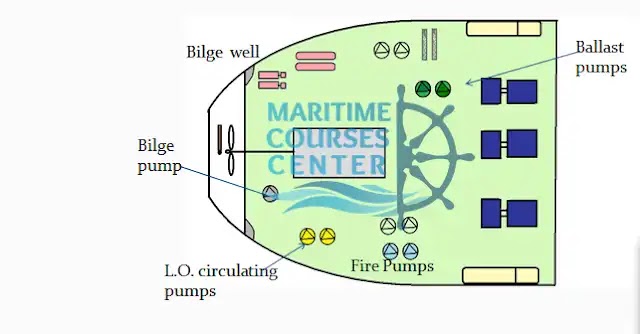
supplying oil to lubricate engines’ moving parts.
Ballast Pumps:
filling & discharging ballast tanks.
Bilge pumps:
collecting & transferring leakages to bilge holding tank.
Fire pumps:
Pumping sea water to fire line.
Domestic F.W. pumps:
pumping fresh water to accommodation fresh water line.
Boilers:
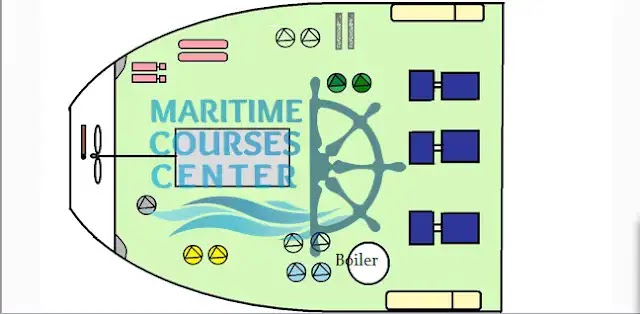
Most ships have boilers which are steam generators, Steam is used mainly in heating of fuel oil , accommodation and other purposes .
Oily water separator:
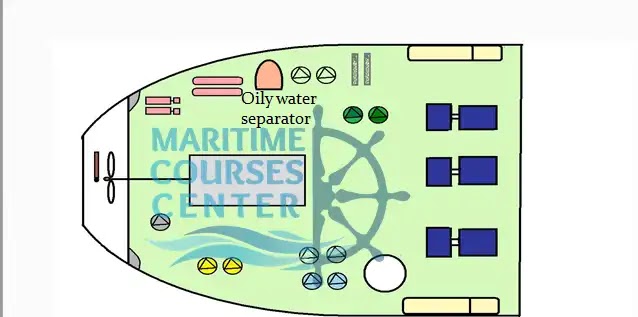
All ships over 400GT should have oily water separator according to IMO requirements , the equipment should be able to separate the oil from water and allow the water to pass with max. 15ppm oil in water .
Sewage Plant:
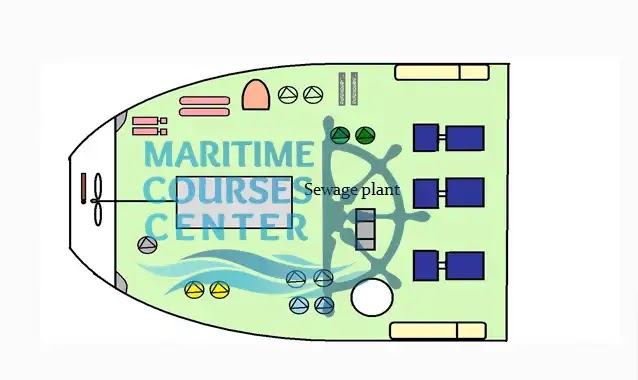
Most ships have sewage plant which is treating sewage biologically before pump it out to sea.
F.W. Generator:
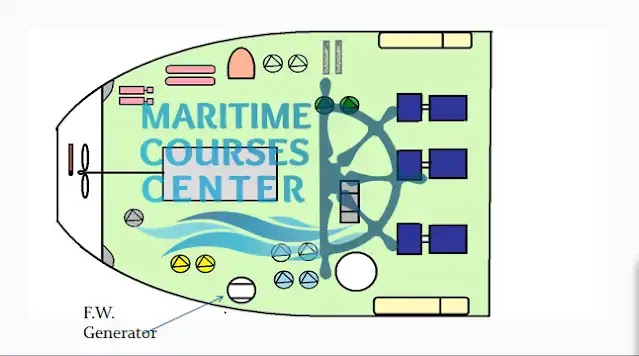
This equipment produce fresh water from sea water.
Incinerator:
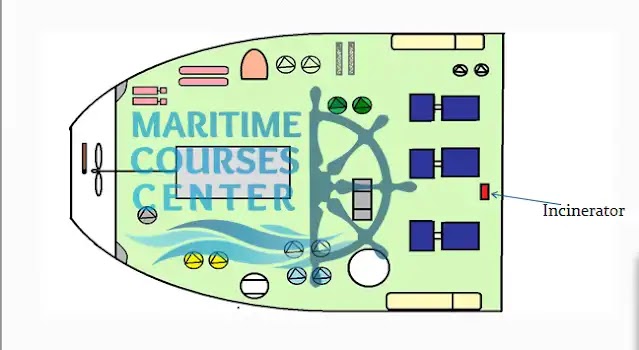
Used onboard ships to incinerate food waste and sludge .
Purifiers:
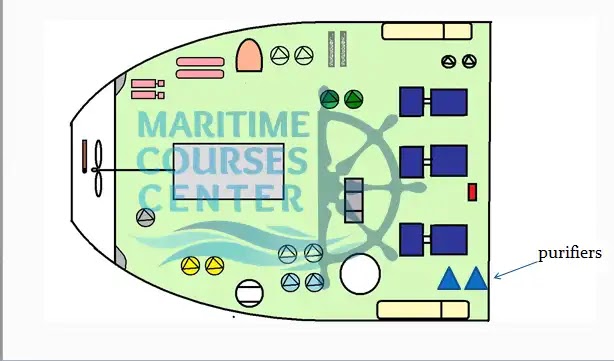
Used for purification of fuel oil, diesel oil and lubricating oil . They Separate solid (dirt) & water from oil.
Heat ex-changers :
1- coolers:
used to transfer heat from hot liquid to cool liquid to cool the hot one . Coolers are used to cool fresh water which is used to cool main engines and generators , also coolers are used to cool lubricating oil and scavenge air
2- Heaters:
used to heat liquids like fuel and domestic fresh water.
Heat ex changers are divided to two kinds :
1- shell & tube type. 2- plate type
Purification of fuel onboard:
Most large marine main engines use heavy fuel oil which need to be purified from water and sludge before using it . There are three steps to do that:
1- Settling:
F.o. transfers from F.O. storage tanks to F.O settling tank which has slightly listed bottom , heating of the fuel in settling tank will separate some of water and sludge then settle it in bottom of the tank and will be collected from lower end of the tank bottom by bushing spring valve and goes to sludge tank .
2- Purification:
After the fuel gets partly cleaned in settling tank it goes to the purifier which will separate most of the water and sludge remains in the fuel.
Purifier is a machine consists of many conical shape plates fitted on a shaft turns with high speed in a bowl, the centrifugal force will act to separate heavy particles to the outer area of the bowl then water will be more closed to the center and the oil will in the center and will be transferred to F.O. service tank .
3- filtration:
before the fuel enters to the engine it pass through F.o. fine filters to filtrate the fuel from fine dirt passed from the purifier.
Note :- heating of heavy fuel oil should take place in all purification processes.
– diesel oil and lubricating oil can be purified in same way.
what is u003cuu003eu003cstrongu003eClassification u003c/strongu003eu003c/uu003eu003cstrongu003eu003cuu003eof shipsu003c/uu003eu003c/strongu003e ?
1u003cstrongu003e-According to usage:u003c/strongu003eu003cbru003eCargo ships – passenger ships – service ships – fishing ships – military ships – pleasure boatsu003cbru003eu003cstrongu003e2- According to manufacturing materials:u003c/strongu003eu003cbru003eu003cbru003eThe main material which is used for building is considered as classification type such as wooden ships, steel ships, fibre glass boats, aluminium boats, and rubber boats.u003cbru003eu003cstrongu003e3-according to engine type :u003c/strongu003eu003cbru003eShips’ main engines could be Diesel engines, Steam turbine, Gas turbine, electric, nuclear, or wind driven ships.u003cbru003eu003cstrongu003e4- According to thrust type:u003c/strongu003eu003cbru003eSail boats, jet boats, rowing boats, and ships with propellers.u003cbru003e u003cstrongu003e5- According to sailing area:u003cuu003eu003cbru003eu003c/uu003eu003c/strongu003eu003cbru003eRiver ships, coastal ships, overseas ships .
What u003cstrongu003eu003cuu003eAre Types of shipsu003c/uu003eu003c/strongu003e ?
u003cstrongu003eGeneral cargo ships:u003c/strongu003e carry dry cargo ( general cargo)u003cbru003eu003cstrongu003eContainer ships:u003c/strongu003e carry containersu003cbru003eu003cstrongu003eBulk ships:u003c/strongu003e carry free fall cargo like grain and coalu003cbru003eu003cstrongu003eRo-Ro ships ( car carrier ships):u003c/strongu003e carry cars and trucks u003cbru003eu003cstrongu003eLife stock carriersu003c/strongu003e: carry life animals like sheep, goats, and cows.u003cbru003eu003cstrongu003eOil tankers:u003c/strongu003e carry crude oilu003cbru003eu003cstrongu003eRefrigeration ships :u003c/strongu003e carry refrigerated and frozen cargo.u003cbru003eu003cstrongu003eLNG ( liquefied natural gasu003c/strongu003e ): carry compressed natural gas in low temperatureu003cbru003eu003cstrongu003ePassenger ships:u003c/strongu003e carry people and their cargo
What Is u003cstrongu003eu003cuu003eEngine room layoutu003c/uu003eu003c/strongu003e ?
The ship is divided to compartments separated by bulkheads .u003cbru003eEngine room is one of these compartments , mostly located aft of the ship.
what is the u003cstrongu003eMain Engine and propeller shaftu003c/strongu003e ?
Main engine produce a torque which is transmitted to the propeller through propeller shaft, The thrust from the propeller is transmitted to the ship’s hull through thrust block and causes the ship to be propelled in the direction of the thrust .

WishlistRead More
MCC
Ship stability LECT 1
MCC
(0 review)
271
students
0
$20.00

WishlistRead More
MCC
Celestial Navigation & Ship stability ( Basic )
MCC
(0 review)
39
students
0
$68.00
WishlistRead More
MCC
COURSE TITLE Introduction to Navigation ( Basic for chart work )
MCC
(0 review)
211
students
0
$400.00

WishlistRead More
MCC
TERRESTRIAL NAVIGATION ( Sailing )
MCC
(0 review)
102
students
0
$100.00

WishlistRead More
MCC
Cargo Calculations Live lecture
MCC
(0 review)
221
students
0
$20.00

WishlistRead More
MCC
Celestial Navigation Basics
MCC
(0 review)
239
students
0
$36.00

WishlistRead More
MCC
Ship stability LECT 2
MCC
(0 review)
358
students
0
$12.00

WishlistRead More
MCC
LSA CODE
MCC
(0 review)
367
students
0
Free
check our free lectures on our facebook page Marine Courses Center
Check also our related course for OOW and For 2nd Mate and chief Mate
- Ship stability LECT 1
- Ship stability LECT 2
- Celestial Navigation LECT 1 | The Concept Of Celestial Sphere
- Celestial Navigation LECT 2 | Systems Of Coordinate Of Celestial Sphere
- Celestial Navigation LECT 3 | Systems Of Coordinate Of Celestial Sphere
- Celestial Navigation LECT 4 | Systems Of Coordinate Of Celestial Sphere Part 3
- Celestial Navigation LECT 5 | Chapter 3 Diurnal motion Celestial Navigation
- Celestial Navigation LECT 6 | Chapter 4 Annual Motion
if you have any question kindly please contact with me via ICQ and here how to contact with me via ICQ click here



