types of boats | types of ships | types of boats and ships | different types of ships and boats | different types of boats
Main types of ships
Ships fall into groups (such as merchant ships, fishing ships, warships and special purpose ships) according to the purpose for which they were built.
merchant marine ships | merchant ship
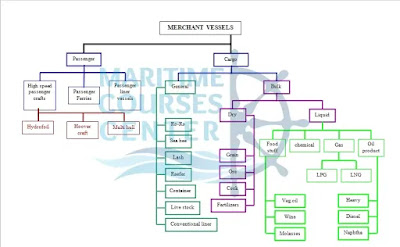
Merchant vessels are built for economic use; they are categorized mainly into two categories, PASSENGERS and CARGO
(vessel other than passenger)
A. Passenger Ships

·: left;”>
·: left;”>
· The carrying capacity is around (1200-5000) Passengers.
· Speeds are usually high in the range of 22-25 knots.
· Ocean-going ferries are combination of roll-on roll-off and passenger vessels.
B. Ferry boats

Those ships assigned to carry passengers in coastal waters.
They are not included in the category of Passenger ships but called ferry boats.
C. Semi Cargo ships
Ships designed to carry cargo as well as passengers are called semi cargo ships. Emigrant ships are included in this group.
D. Cargo Ships

Cargo ships are built exclusively for carrying cargo and all spaces aboard other than that for crew accommodation or required for the ship’s operation is assigned to the carriage of cargo.
Cargo ships are further divided into four groups:
1. There are cargo liners: which give regular services, sailing
fixed schedules.
fixed schedules.
2. Trampers: which operate without any fixed time schedules
or regular ports of call but which respond to the market situation
anywhere in the world.
or regular ports of call but which respond to the market situation
anywhere in the world.
3. General cargo ships: are capable of carrying various general cargoes except that specified as special cargo.
4. Special cargo ships: are built, specially constructed and
equipped to carry a specified cargo.
4. Special cargo ships: are built, specially constructed and
equipped to carry a specified cargo.
5. They are broken down into:
Oil Tankers

· It is designed to carry crude oil from oil fields to discharging ports.
· The large tanker is the VLCC (Very Large Crude Carrier) and ULCC (Ultra Large Crude Carrier).
L.P.G. – L.N.G. Carriers


· The Liquefied Petroleum Gas and the Liquefied Natural Gas is designed to carry the Gas [in liquid form at atmospheric pressure (about 17 bars) and a temperature in the region of (-40 & -164oC)
· It has double hull construction, cargo pumping arrangements and it has no derricks but has a small boom to fix the hose.
Ore Carriers

· A vessel designed to carry materials in its natural state such as copper, iron, coal etc.
Grain Carriers

· A vessel to carry all types of grain in bulk state.
· It has large hatches to facilitate rapid and simple cargo handling.
Cement Carriers

· A vessel designed to carry cement in bulk state.
· They trade between special terminals, which have particular equipment for loading and unloading bulk commodities (shooters).
Refrigerated Carriers

· It is designed to carry refrigerated / frozen cargo in insulated holds at low or very low temperatures.
· This vessel is faster than cargo ship.
Fishing Ships

Ships involved in fishing industry are called fishing ships.
Warships

Ships built for the defence of nation are called warships. They include: battleships, cruisers, aircraft carriers, destroyers, submarines, etc.they have no plimsoll mark or load line. they are usually painted in Gray colour.
Training Ships
· It is designed to train cadets to be officers or Engineers onboard ships.
A vessel equipped with different modern training equipments. Used in the training program.
Cable Laying Ships

A vessel designed for laying and maintaining cable at seabed, such as telephone cable, electricity cable etc.
Salvage boats

· It is a tug-boat designed with salvage equipment (towing wires, towing hook – shackles etc.)
· Usually have powerful engines and high stability.
Dredgers

·: large;”>
Ice breakers

· A vessel designed for breaking ice in frozen ports.
· It is constructed with hardened bow equipped with ice-breaking machinery.
Tug boats

· It is designed for towing ships in ports during berthing ,
UN-berthing and shifting operations according to pilot advice.
UN-berthing and shifting operations according to pilot advice.
· It has a very powerful engine.
Pilot boats

· It is a boat that provides the pilotage service to the ships entering or leaving ports.
Containers ship

· It is designed for the carriage of general cargo special steel units called containers with length (20 – 40 feet). Providing from door to door service.
Ore/Bulk/Oil Ship (O.B.O)

·: ltr; line-height: 150%; margin: 0in 0.25in; text-align: center; text-indent: -0.25in; unicode-bidi: embed;”>
RO/RO (Roll on / Roll off) ships

· This ship are designed with facilities for quick loading and discharging cargo on wheels – so that car drivers themselves can drive in and out through hydraulically operated bow or stern Ramps (special doors).
Lash ships (Lighter Barges carrier)

·: ltr; line-height: 150%; margin: 0in 0.25in; text-align: center; text-indent: -0.25in; unicode-bidi: embed;”>· Vessels of this type are very large, low ships with no sheer and very little superstructure.
·: ltr; line-height: 150%; margin: 0in 0.25in; text-align: center; text-indent: -0.25in; unicode-bidi: embed;”>· In port they are lifted from the stowed position, lowered to water level and stowed without the use of Quay space.
Light Vessels

·: ltr; line-height: 150%; margin: 0in 0.25in; text-align: center; text-indent: -0.25in; unicode-bidi: embed;”>· It is usually found at areas where light houses cannot be built and this area have shallow depths.
Floating Dock ship
· A vessel designed as a floating dock. It is used for lifting vessels to carry out under water repairs on these ships.
Sea Base

· Is somewhat larger than the LASH ship and carries 38 barges.
· Each barge may be loaded with up to 1000 tones of cargo.
· The barges are stowed onboard by an elevator located at the stern.
Car Carrier

·!–[if gte mso 9]> 800×600
Floating Crane

· Used for loading / unloading heavy cargo and salvage work at sea.
Hovercraft
· The hovercraft introduces a new principle as far as ships are concerned.
· In the hovercraft the support is generated by an air cushion created by blowing air out of a curtain or skirt surrounding the boat.
Propulsion is usually, but not necessarily, generated by means of airscrews
Hydrofoil boats
· Hydrofoil boats make use of the same principle involved in the flight of aircraft.
· Hydrofoils are attached to the bottom of the ship by means of struts, and the ship moves through water. A lifting force is generated just as the force generated when an air plane wing moves through the air.
Y. Multi-hull ships
· They are usually catamaran or occasionally tri-maran. The arrangements using two or three hulls placed parallel to one another and some distance apart, connected by a bridge structure.
·: large;”>
Z. Life Stock Ships
· A vessel has special design with high ventilated holds used for transport of life stock (sheep, goats, bulls and buffaloes).
· It is equipped with drinking and feeding systems


